Clamp meters were popular among AC electricians as these instruments were invented. However, due to its diversity in functions and new advancements, clamp meters become popular equally among AC and DC electricians.
Hence, clamp meters gained their fame due to their safe and accurate reading in both AC and DC applications. A step further, a single clamp meter can perform many tasks as posed by modern challenges.
The basic differences between AC and DC clamp meters lie in their application, circuitry, structure, function, and capabilities. Each works on a different method, for different circuits, using different approaches, and having different internal circuits. Likewise, the compatibility of both is associated with their corresponding current type.
Let’s learn in more detail how these two clamp meters are different from each other.
What are the Differences Between AC and DC Clamp Meters?
As obvious from their names, AC clamp meters are designed for AC circuits and are suitable for our domestic use. DC clamp meters are compatible with DC circuitry.
Let’s talk about both types of clamp meters and the differences between them.
Differences between AC and DC clamp meters
The key difference between AC and DC clamp meters lies in their internal circuitry. Their internal circuit is quite different from each other.
To understand both, we should study each in detail and understand their circuitry. Let’s learn about them in detail.
AC Clamp Meters
AC clamp meters help us find current in AC wiring. It replaced the old method in which we disconnected the circuit and attached the multimeter in series.
Clamp meters are primarily designed for measuring high-voltage AC without disconnecting the main wiring. We can say the prime concern behind the design of the clamp meter for AC is safety and accuracy.

Let’s learn more about the AC clamp meter.
1. Working Principle
These clamp meters work on the principle of electromagnetic induction. Simply put, the principle says that alternating current (with variable polarity) induces current in a nearby coil due to a change in electromagnetic field.
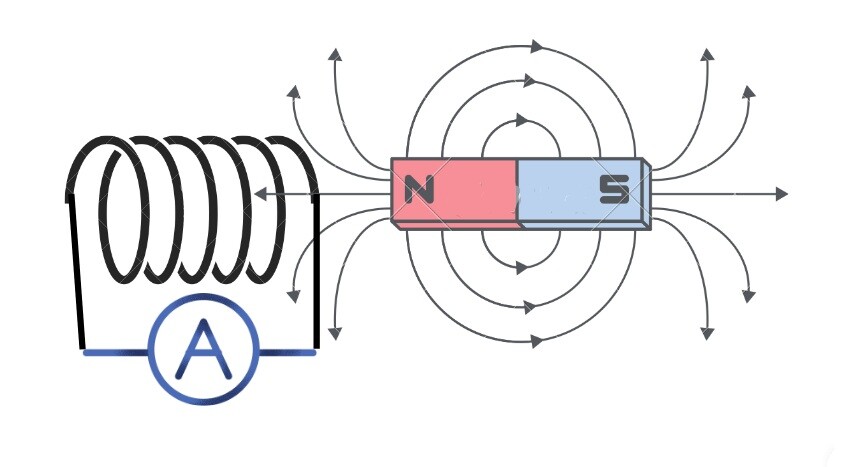
Hence, that induced current is further processed and ascertained. For more detail visit the following link.
2. Application
Likewise, AC clamp meters are used in domestic, industrial, and any type of AC installation. The range of its users is diverse because of its safe and simple method of usage.
These clamp meters are equally effective for high voltage and high current.
3. Internal Circuitry
As we mentioned earlier clamp meters work on the principle of electromagnetic induction. Hence, separate processing circuits condition the induced current for display.
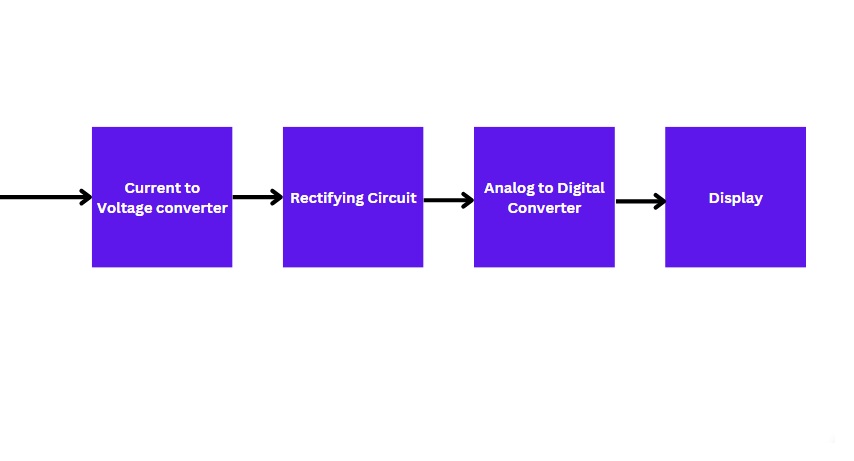
Generally, every AC clamp meter has this basic method of processing the signal (as mentioned in the image).
4. Functions
Similarly, AC clamp meters are equipped with the relevant functions. We can measure the frequency of the signal, impedance, RMS value, zero crossing, and more important parameters necessary for AC analysis.
Hence, good AC clamp meters explain everything about the AC circuit.
DC Clamp Meters
The manufacturer designed DC clamp meters later than AC clamp meters. As DC is constant, the electromagnetic induction failed to work here. Although, the user felt the need for a DC clamp meter.

Hall’s effect solves this problem. Through this, we can detect DC without physical contact with the current carrying wire. It helped us design the DC clamp meters which play an essential role in DC circuits.
Especially, when the high-voltage DC was introduced, the importance of DC clamp meters boosted.
Let’s study more about DC clamp meters.
1. Working Principle
DC clamp meters follow the principle of Hall’s effect. When a current-carrying wire is brought near the Hall’s sensor, it produces a potential difference in the sensor.
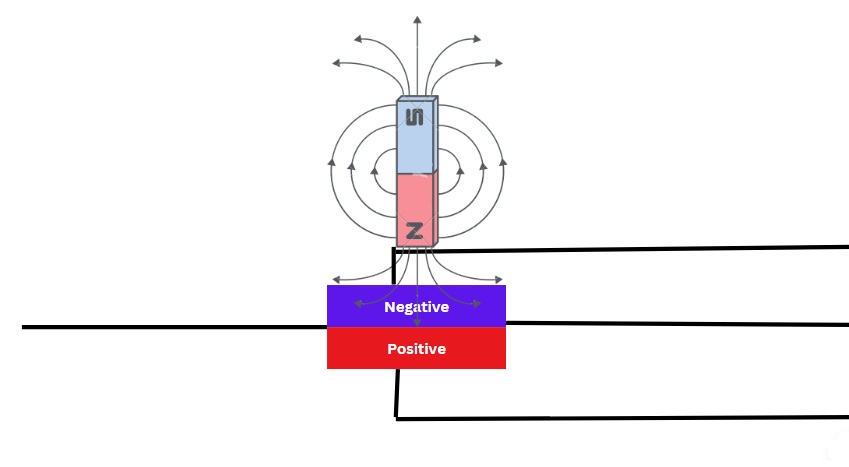
This potential difference is generated due to the pushing of positive and negative charges on the sensor due to the electromagnetic field of the current-carrying wire.
The same potential difference is passed to the conditioning circuit for further processing.
2. Application
We can use DC clamp meters in DC-powered circuits. These circuits may be powered by a battery, solar panel, or fuel cell.
Whatever the source may be, the DC clamp meter can easily measure the DC without disturbing the main circuit.
Solar panel systems, DC power plants, the Automobile industry, and research laboratories are suitable workplaces for a DC clamp meter.
3. Internal Circuitry
The core part of a clamp meter is its internal circuitry. It depends on the input and output signal of an instrument. A DC clamp meter senses current in potential difference and displays the value on a digital LCD.
As obvious, we are going to process voltage not current, hence the internal circuitry should be according to voltage not current. This is one of the major differences between DC and AC clamp meters.
Here, the step of current-to-voltage conversion is bypassed as the input to the internal circuit is already a voltage.
4. Function
DC clamp meters have the function of measuring DC voltage, Resistance, Capacitance, testing diode, etc. These functions help us to analyze the DC circuit and its components.
After a brief discussion, let’s compare these two clamp meters through the table below.
Comparison Between AC and DC Clamp Meters
We discussed each clamp meter in detail in the above section. We gained sufficient knowledge about both. Now, we will compare both to get more information about these clamp meters.
Before comparing both, we must tell you that nowadays clamp meters are equipped with both circuitry. These clamp meters can measure AC and DC with just a little turn of the knob.
Let’s go through the comparison table.
| S. No | Parameters to check | AC Clamp meter | DC Clamp meter |
| 1 | Working Principle | EM Induction | Hall’s Effect |
| 2 | Applications | Common | Specific |
| 3 | Internal Circuit | With Current to Voltage Converter | Without Current to Voltage Converter |
| 4 | Measuring Frequency | Yes | No |
| 5 | Induced Signal | Current | Voltage |
| 6 | Zero Crossing | Yes | No |
| 7 | RMS reading | Yes | Optional |
As given in the table, these are the key differences between AC and DC clamp meters.
We can say that the method sensing of current, application, processing, associated functions, and internal circuitry of both are different from each other.
Conclusion
AC clamp meters are manufactured before DC clamp meters. The prime function of AC clamp meters is to measure AC safely. However, technological advancement extended its functions to DC and other functions.
AC clamp meters work on the principle of electromagnetic induction. In this method, the current-carrying wire induces a current in the coil of the clamp meter. The signal is forwarded for further conditioning.
On the other hand, the DC clamp meter senses current through Hall’s effect. Hall’s sensors work on the principle of Hall’s effect. The existence of a magnetic field produces potential differences.
Applications, working principles, circuits, and functions of both are different from each other. These differences also have a significant effect on the structure of these clamp meters.
As we compare both, we get the idea that AC clamp meters have all the functions that are necessary for AC analysis. The same is true for DC clamp meters.
Both clamp meters work well in their corresponding area. However, every user must know the proper method of its use. In this way, we can get more benefits from these clamp meters.
Other useful posts:
